The Indian Rupee (INR) and the US Dollar (USD) dance a constant, often unpredictable, financial tango. When the INR weakens against the USD – a situation known as INR depreciation – it sends ripples through the Indian economy. But why does this happen, and more importantly, what does it mean for you? Let’s dive in, not just reporting what is happening, but explaining why it matters, especially for us here in India.
Understanding Currency Depreciation | The Basics
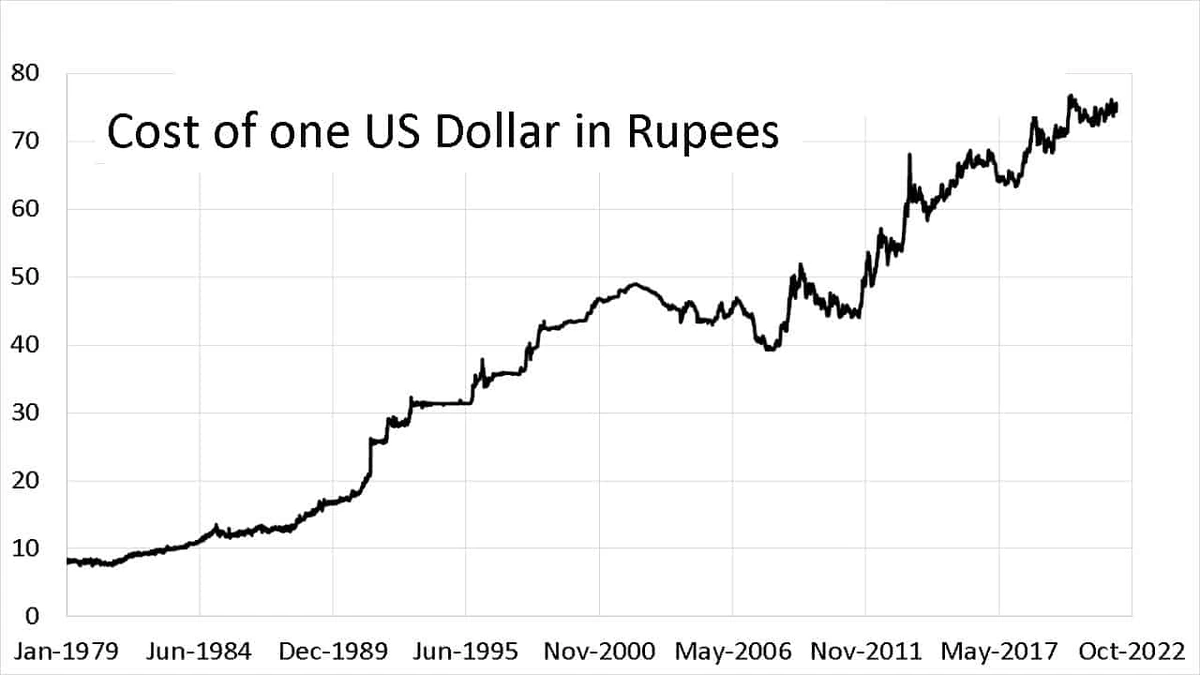
Before we get to the nitty-gritty, let’s clarify what currency depreciation actually is. Simply put, it means the Indian Rupee buys less USD than it used to. Imagine you could buy 80 Rupees’ worth of USD last year, but this year, you need 83 Rupees to get the same amount. That’s depreciation in action. There are various factors affecting currency value. The forex market is volatile, and understanding these fluctuations is key for investors and businesses alike.
But what causes this? Well, several forces are usually at play. Think of it like a tug-of-war between factors that strengthen the Rupee and those that weaken it.
4 Key Reasons Behind INR Depreciation
Here are four major reasons why the INR might depreciate against the USD INR :
1. Demand and Supply Dynamics
This is Economics 101, but it’s fundamental. If there’s a higher demand for USD in India than there is for INR, the price of the dollar goes up, and the Rupee weakens. Why might demand for USD increase? Indian companies might need dollars to pay for imports, or investors might be pulling their money out of India to invest elsewhere. Several factors affecting currency value, including import costs, could increase demand for USD.
Here’s the thing: India relies heavily on imports, especially oil. When global oil prices rise, Indian companies need more USD to buy the same amount of oil, driving up demand and potentially causing depreciation. It’s a vicious cycle, honestly.
2. Inflation Differential
Inflation – the rate at which prices are increasing – plays a huge role. If India’s inflation rate is higher than that of the US, Indian goods become relatively more expensive compared to American goods. This can lead to a decrease in demand for Indian exports and an increase in demand for imports, again putting downward pressure on the Rupee. Managing inflation is vital for maintaining currency stability.
And let’s be honest, nobody wants their money to buy less than it used to. High inflation erodes the value of savings, and that’s something everyone in India feels directly.
3. Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rates also have a significant impact. If interest rates in the US are higher than in India, investors might be tempted to move their money to the US to earn a higher return. This outflow of capital from India increases the demand for USD and weakens the Rupee. Governments use interest rates to try and control inflation.
I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized it’s not just about the absolute interest rate, but also the perception of risk. Investors need to feel confident that their investments in India are safe and secure.
4. Global Economic Uncertainty
When there’s turmoil in the global economy – a financial crisis, a pandemic, geopolitical tensions – investors often flock to safe-haven currencies like the USD. This increased demand for the dollar further strengthens it against currencies like the INR. Events that affect global trade, such as trade wars, can also impact currency values.
Think of it like this: in times of uncertainty, people want to hold onto something they perceive as stable and reliable. The US Dollar, despite its own ups and downs, is often seen as that safe bet.
Impact on the Indian Economy and You
So, what are the consequences of a weaker Rupee? Well, for starters, imports become more expensive. This means everything from electronics to crude oil costs more in Rupee terms. This can lead to higher inflation and impact the common person’s pocket. On the other hand, a weaker Rupee can boost Indian exports, making them more competitive in the global market. This can benefit Indian companies and create jobs. You should read this article about the Reliance group’s financial troubles.
Here’s why this matters: For students planning to study abroad, a weaker rupee means that tuition fees and living expenses in dollar terms will be significantly higher, potentially derailing their plans. For businesses that import raw materials, it translates to increased costs and potentially lower profit margins. And for the average Indian consumer, it might mean paying more for everyday goods and services.
What Can Be Done?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) can intervene in the foreign exchange market to try and stabilize the Rupee. They can buy Rupees and sell dollars to increase the demand for the Rupee and reduce its depreciation. However, this is not a long-term solution, as it can deplete India’s foreign exchange reserves. A more sustainable approach involves addressing the underlying economic factors that are causing the depreciation, such as controlling inflation and promoting exports. Government policies play a crucial role in economic growth .
Let me rephrase that for clarity: The RBI’s interventions are often like putting a band-aid on a much deeper wound. While they can provide temporary relief, they don’t address the root causes of the problem.
The Global Context of Currency Fluctuations
It’s crucial to remember that currency fluctuations are not unique to India. All currencies are subject to market forces, and their values rise and fall relative to each other. The USD to INR rate is just one piece of a much larger global puzzle. Keeping an eye on global economic trends is vital for understanding currency movements.
FAQ Section
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current USD to INR exchange rate?
The exchange rate fluctuates constantly. You can find the latest rate on financial websites like Google Finance, or reliable currency converter tools.
How does INR depreciation affect remittances?
For Indians living abroad and sending money home, a weaker Rupee means their remittances are worth more in Rupee terms.
Is INR depreciation always bad for the Indian economy?
Not necessarily. While it can increase import costs and inflation, it can also boost exports and make India more competitive.
What role does the RBI play in managing INR depreciation?
The RBI can intervene in the forex market by buying Rupees and selling dollars, but this is usually a short-term measure.
Ultimately, understanding the reasons behind currency depreciation – whether it’s related to trade balance or global financial events – is essential for informed financial planning and decision-making. The interplay of forex rates and economic stability is a complex issue.